In today’s highly competitive risk market, an effective risk management strategy is more essential than ever.
Regardless of industry, being prepared for what can happen throughout a project ensures that you are well prepared to lead your team to successful execution.
As companies focus more on identifying, managing, and monitoring risks in response to a more dynamic risk environment, you may have questions about developing a risk management strategy and what risk management techniques you can use.
Here’s all you need to know to address today’s major risks adequately address today’s significant risks.
Featured Reading:
What is Risk Management?
Risk management identifies, assesses, and controls hazards to an organization’s capital and income. Various factors, including financial instability, legal responsibility, technology difficulties, strategic management failures, accidents, and natural disasters, cause these risks.
A good risk management technique may help a company analyze all its risks. Risk management also looks at the relationship between risks and the potential repercussions for a company’s strategic goals.
Why is Risk Management Important for Organization?

Most businesses face project or operational risks, but having risk management techniques and strategies in place is crucial for identifying your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) — often known as doing a SWOT analysis. There are various additional benefits to effectively managing risks.
1. Business and Process Efficiency
No matter how well-prepared your organization is, operational risks can occur at any time and from unexpected sources. Risks include a new cybersecurity threat, a supplier or service provider that can no longer assist your firm, and equipment failure.
With all dynamic variables within and outside of a company that might have an influence, it is critical to have a clear risk management framework and plan in place that allows you to verify internal controls to avoid fraud — or to deal with other forms of risk as they occur.
2. Asset Protection for Your Business
Protecting your company’s assets, whether physical equipment, supplies, or information, is critical.
It consists of identifying security risks and creating methods to solve them. These methodologies include determining the likelihood of known threats, how these attacks may exploit any weaknesses in your security systems, and the possible impact on your business.
3. Customer Satisfaction
Your corporate logo, brand, digital presence, and reputation are all assets that your customers like seeing and interacting with regularly. Customers can trust your reputation and brand if your company has a well-thought-out and implemented risk management technique.
By safeguarding these assets, your risk policies and procedures help you protect your brand and reputation. It also guarantees that clients are confident in your capacity to present and deliver the goods and services you promised. As a result, consumer happiness and loyalty are higher.
4. Enables Growth
Successfully managing risks is crucial to finishing projects on time and getting the required results. Risk identification, evaluation, and management methods reveal risks faster, allowing your firm to remove projects and activities that simply do not provide a return on investment. This increases your chances of attaining your forecasted project portfolio and overall business performance targets and reaping the benefits.
5. Improved Budgeting
The majority of businesses are focused on profit. When a breach happens, it generally has a major financial impact, and it usually necessitates many hours spent working with legal and insurance teams to conduct comprehensive investigations. Managing market, credit, operational, reputational, and other risks is crucial to your firm’s success.
6. Keeping Competitiveness
Risk management helps firms reduce losses during critical occasions. Poorly managed enterprises are currently battling to stay afloat. On the other hand, companies that exercise risk management tend to lower their losses. As a result, such firms’ Competitiveness remains steady. It may become better.
Diverse departments and stakeholders must also actively interact with one another in risk management systems. When negative events, such as recessions, companies with stronger risk management policies stay afloat and have a substantial cash reserve.
This is why, during a crisis, certain firms appear to have more money to make acquisitions.
Risk Management Techniques to Use in 2023

1. Risk Identification
Risk identification can occur through
- passive vulnerability discovery or
- Through the deployment of technologies and management systems that raise red flags when potentially identified threats exist.
Being proactive rather than reactive is always the greatest way to reduce risk. To detect risks ahead of time, apply the risk management strategies listed below.
a. Decision Tree
When presented with various possibilities, decision trees are utilized to make decisions. It enables you to evaluate the importance of outcomes and the likelihood of reaching them. This, in turn, aids in making a more informed selection.
1. Create a decision tree for a project management issue by listing all choices.
2. Assign each risk a chance of occurrence
3. Assign a monetary value to the outcome of a risk
4. Calculate each option’s Expected Monetary Value (EMV)
b. Influence Diagram
Decision trees and influence diagrams are inextricably linked and are commonly used in combination. An influence diagram is a graphical depiction of the information in a decision tree. It employs four types of variable notation: selection (a rectangle), chance (an oval), objective (a hexagon), and function (a rounded rectangle). In addition, solid lines are utilized to demonstrate influence in influence.
There are several approaches to creating an impact diagram. They can be created using a pen and paper, a whiteboard, or, more efficiently, diagramming software.
- Make a rectangle in the page’s upper-left corner. This is the very first “node” or shape
- Fill in this rectangle with the first question or condition that leads to a choice
- Using the decision tree as a guide, add additional shapes to the page, labeling each one
- A series of decisions, functions, and chances should all contribute to the achievement of a goal
- To represent the flow of influence, use a combination of straight and angled lines with arrowheads
2. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis, often known as the SWOT matrix, is a risk management technique used by project managers and businesses. SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) is a term that stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
It is a framework through which businesses and teams assess the possible internal and external variables that may have a positive or negative impact.
Here are some recommended steps for measuring strengths
- Brainstorm and note comparable strengths
- Analyze and collect appropriate strengths
- Strengths should be prioritized using a forced rank order or the nominal group technique
- For vulnerabilities, opportunities, and threats, repeat steps 1-3
- Establish the strategy
For strategy
- Develop techniques for minimizing weaknesses and avoiding dangers
- Define tactics that capitalize on strengths to avoid risks
- Define tactics that use strengths to take full advantage of available opportunities
- Define tactics for capitalizing on opportunities while overcoming shortcomings

Analyze The Identified Risk
After identifying the risks, the next step is to evaluate them to determine their impact on your business and existing projects. If you properly assess the risks, you can prioritize which ones impact your business most.
Risk analysis may be approached in two ways.
Risks are analyzed qualitatively based on their likelihood of occurrence and impact on projects, enterprises, etc.
Quantitative risk analysis examines probable outcomes and determines the chance of achieving objectives.
The risk management approaches listed below might help you with your analysis.
Several risk analysis methodologies are available to help managers with the analysis and decision-making process. Some of these needs using risk assessment tools such as charts and papers. Let us look at these risk analysis methods and how they might help you.
1. Bow Tie Analysis
This qualitative risk analysis technique determines the causes and consequences of all potential project risks. Before evaluating causes, ramifications, and, most importantly, risk mitigation measures, the project management team must first identify possible risks to the project. It is a very versatile method that may be used in any industry.
2. Risk Analysis Matrix
The risk analysis matrix assesses the likelihood and severity of dangers and prioritizes them. It is characterized as a qualitative risk analysis tool since risk probability is calculated on a relative scale rather than a statistical scale.
Its major purpose is to help managers prioritize risks and establish a risk management plan that includes the necessary resources and risk reduction methods.
3. Risk Register
A risk register is an important project management tool for recording project risks. It is a document that provides vital information on all potential dangers that may arise during the project execution phase.
It is meant to be used as input for the risk management plan, which specifies who is responsible for the risks, risk mitigation techniques, and resources needed. Developing a risk register frequently necessitates the utilization of many reliable information sources, such as the project team, subject matter experts, and historical data.
4. SWIFT Analysis
SWIFT is an abbreviation for Structured What If Technique. It is a risk analysis method that recognizes potential risks associated with project plan changes. Team members are required to attend, as the name indicates.
Responding to Risk
After identifying and analyzing the risk, the project team develops a risk mitigation plan. This is a method for limiting the implications of an unexpected event. Risks are mitigated by the project team in several ways, including:
- Avoiding Risk
- Risk distribution
- Risk Reduction
- Risk transfer
Each of these risk-mitigation strategies can be an effective technique for minimizing particular risks as well as the overall risk profile of the project. The risk mitigation plan outlines the risk mitigation approach and steps for each identified risk event.
Risk avoidance often entails devising an alternate method with a better likelihood of success but a higher cost associated with completing a project assignment. Using established and current technologies rather than adopting new techniques is a typical risk avoidance approach, even if the new techniques promise higher performance or lower prices.
Risk sharing requires working with others to share responsibility for potentially harmful activities. Many organizations that work on international projects will reduce the political, legal, labor, and other risks associated with those projects by creating a joint venture with a company in that country. When the other firm possesses expertise and experience that the project team does not, collaborating with another company to share the risk associated with a portion of the project is beneficial.
Risk Reduction is a monetary outlay made to reduce the risk of a project. To avoid the risk of currency exchange rate fluctuation, companies may routinely get currency rate assurances on international projects. To enhance trust in the plan and decrease project risk, a project manager may hire an expert to examine technical plans or cost estimates on a project. Another risk-mitigation method is to deploy highly skilled project people to the project.
Risk transfer is a risk-mitigation approach in which the risk is shifted from one entity to another. Purchasing particular insurance is a risk-transfer technique. Risk transfer is a popular risk management strategy that involves transferring the potential loss from an unfavorable event to a third party. The individual or corporation will usually make monthly payments to the third party to compensate it for absorbing the risk.
What Are the 4 Strategies for Risk Management?
1. Avoidance:
When using the risk avoidance strategy, organizations look to completely avoid any activity or environment which could potentially bring about risks. This is done by removing all associated activities and/or potential sources of risks from an organization’s operations and processes.
2. Transference:
With this risk strategy, organizations look to transfer their potential losses to a third party such as insurance companies or banks in return for some amount of premium payment or fee paid by them periodically over time. This helps reduce the financial burden on the organization should any risks occur.
However, it also gives away control to the third-party provider who may choose not to cover certain types of losses depending upon their policies and other factors that they consider important while covering these risks in an insurance policy.
3. Mitigation:
Under mitigating a risk strategy, organizations can sometimes reduce their exposure to any particular type of risk through developing preventive measures such as implementing proper safety protocols at work sites and investing in robust cyber security solutions for better protection against online threats, etc.,
So that if something does happen then its impact on the business is minimized or contained within acceptable limits through prompt action taken ahead of time rather than reactionary methods used afterward when damage has already been done.
4. Acceptance:
The last risk management strategy involves accepting that no matter what plans have been made sometimes things do go wrong despite our best efforts at prevention due to which there is always some residual level of uncertainty present even after taking all necessary steps beforehand towards containing any possible future mishaps resulting from the same.
This means that eventually, we have no choice but to accept our fate come what may no matter how hard we try at preventing it in case things do go wrong causing serious liabilities down the line later on if not prepared well enough initially with respect to unforeseen circumstances arising out of nowhere related directly or indirectly with our own actions unintentionally caused previously.
What is Risk Avoidance?
Risk avoidance is a strategy used to eliminate or reduce exposure to potential hazards, threats, or other risks. It involves recognizing, assessing, and prioritizing the various risks associated with an activity, process, or plan of action and then taking appropriate steps to avoid those risks.
Risk avoidance strategies can include changing the activity altogether, instituting new procedures and policies, providing additional training for personnel involved in carrying out the activity, and implementing safety equipment or monitoring systems to detect issues before they become a problem.
The approach taken will depend on the perceived issue and its severity. Although risk avoidance attempts to eliminate any potential risk associated with an activity it may not always be possible as some activities inherently contain some degree of risk that cannot be avoided without halting progress altogether.
Contingency Plan
The project risk strategy balances the expense of mitigation against the project’s benefit. When a risk event is identified that may obstruct the attainment of a project goal, the project team typically devises an alternate method of accomplishing that goal.
These are referred to as contingency plans.
How to avoid future risks?
Identifying and mitigating potential risks is critical to managing any project or business. To achieve this effectively, it is essential to follow certain steps and strategies that help minimize future risks.
Firstly, conducting a thorough risk assessment is a crucial step in identifying potential risks. A risk assessment involves examining both internal and external factors that could affect the project, such as market trends, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the organization’s capabilities. By understanding these factors, it is easier to anticipate potential risks and plan accordingly.
Secondly, involving stakeholders in the risk identification process is critical. Engaging team members, vendors, customers, and other stakeholders in the process helps to provide a more comprehensive understanding of potential risks and their impact on the project. This collaborative input is valuable in the risk identification process.
Thirdly, prioritizing risks is an important step in mitigating potential risks. Not all risks are equal; some may have a higher likelihood of occurring or more significant consequences. Prioritizing risks based on their potential impact and probability enables the team first to address the most critical risks.
Fourthly, developing risk mitigation strategies is crucial in minimizing potential risks. Creating a plan to either eliminate, reduce, or accept the risk can involve implementing new processes, investing in technology, or reallocating resources.
Fifthly, regularly monitoring risks and updating the plan is critical. Risk management is an ongoing process, and regularly reviewing and updating the risk management plan is essential to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Being prepared to adapt to new risks that may emerge over time is also important.
Sixthly, communication and training are key elements in effective risk management. Ensuring that everyone involved in the project is aware of the risks and their roles in mitigating them is vital. Providing training and resources to empower team members to contribute effectively to risk management efforts is also crucial.
Lastly, learning from past experiences is essential in improving risk management processes and avoiding making the same mistakes in the future. Analyzing past projects, both successes and failures, provides valuable insights into the risk management process, enabling the team to improve their strategies.
Who is responsible for developing a risk management strategy?
Effectively avoiding future risks demands a proactive approach to identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. Here are some valuable tips to help you achieve this:
1. Identifying Stakeholders
Identifying stakeholders is a crucial step in risk management. Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the success or failure of your project. They can affect or be affected by your project’s outcome, making it essential to identify them early on in the process.
Stakeholders can include team members, vendors, customers, shareholders, regulatory bodies, and more. Each stakeholder has unique interests, and understanding these interests helps anticipate potential risks.
For example, if you are building a new e-commerce website for a client, the sales team’s performance and bonuses might depend on the site’s success. Therefore, the sales team becomes a critical stakeholder, and their interest must be factored into the risk management plan.
Identifying stakeholders early on in the project allows for effective communication and collaboration throughout the process. It helps ensure that everyone’s interests are considered, and potential risks are identified and addressed.
Stakeholder identification can be done by reviewing project goals, examining who will be impacted by the project, and identifying potential sources of support or opposition.
Once identified, stakeholders should be engaged and involved in the risk management process. Collaborative input can provide a more comprehensive understanding of potential risks and their impact on the project. It also helps ensure that all perspectives are considered when developing risk mitigation strategies.
2. Conduct a thorough risk assessment.
Regular risk assessments enable you to stay ahead of potential challenges and proactively address them. To conduct a comprehensive risk assessment, follow these steps:
Identify risks: Begin by listing potential risks that may impact your project, including those related to market trends, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and your organization’s capabilities.
Analyze risks: Assess the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk. This analysis will help you prioritize risks and determine the most appropriate mitigation strategies.
Evaluate mitigation strategies: Consider various risk mitigation strategies and evaluate their effectiveness in addressing the identified risks. This evaluation will guide you in selecting the most appropriate strategies to implement.
Implement risk mitigation strategies: Put the selected risk mitigation strategies into action to minimize the potential impact of identified risks on your project.
3. Involve stakeholders in risk identification.
Engaging all stakeholders in the risk identification process is crucial for developing a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and their impact on the project. To involve stakeholders in risk identification:
Communicate the process: Clearly communicate the risk identification process to all stakeholders, highlighting their role in contributing valuable insights and perspectives.
Gather input: Encourage stakeholders to share their concerns, potential risks they foresee, and any relevant experiences that could inform the risk identification process.
Analyze stakeholder input: Review and analyze stakeholder input to determine if any new risks have been identified or if existing risks require reevaluation.
Incorporate stakeholder input into risk assessment: Integrate stakeholder input into the risk assessment process, ensuring that all perspectives are considered when prioritizing risks and developing mitigation strategies.
4. Create an action plan
Developing a detailed action plan is crucial for effectively addressing identified risks and keeping the project on track. To create a comprehensive action plan, follow these steps:
List identified risks: Begin by listing all the identified risks from the risk assessment and stakeholder input.
Assign responsibilities: For each risk, assign a responsible individual or team to manage and address the risk. Ensure these individuals have the necessary knowledge and resources to handle the risk effectively.
Outline mitigation steps: Clearly outline the specific steps that need to be taken to mitigate each risk. These steps should be based on the selected risk mitigation strategies.
Establish timelines: Set realistic deadlines for each mitigation step, taking into account the urgency and potential impact of each risk.
Monitor progress: Regularly review the progress of each mitigation step to ensure timely completion and effectiveness. Adjust the plan as needed based on any changes in risk or project circumstances.
5. Prioritize risks
Not all risks carry the same weight, and it is essential to prioritize them based on their potential impact and probability. To prioritize risks effectively, consider the following:
Evaluate impact: Assess the potential consequences of each risk on the project’s objectives, resources, and stakeholders. The higher the impact, the higher the priority.
Determine probability: Estimate the likelihood of each risk occurring. Risks with a higher probability of occurrence should generally be prioritized.
Create a risk matrix: Use a risk matrix to plot each risk based on its impact and probability. This visual representation will help you identify the most critical risks that demand immediate attention.
Focus on high-priority risks: Develop and implement mitigation strategies for high-priority risks first, allocating the necessary resources and attention to address them effectively.
6. Develop risk mitigation strategies
Creating a plan to eliminate, reduce, or accept identified risks is essential for effective risk management. Consider the following strategies when developing your risk mitigation plans:
Eliminate the risk: Identify ways to completely remove the risk from the project. This may involve altering project plans, changing suppliers, or revising processes.
Reduce the risk: If elimination is impossible, focus on reducing the risk’s impact or probability. This could involve implementing new processes, investing in technology, or reallocating resources.
Transfer the risk: In some cases, transferring the risk to another party, such as through insurance or outsourcing, may be beneficial.
Accept the risk: When risks cannot be eliminated, reduced, or transferred, accept the risk and develop contingency plans to manage potential consequences.
7. Monitor risks and update the plan:
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and updating. To ensure your risk management plan remains relevant and effective, follow these steps:
Review progress: Regularly review the progress of risk mitigation strategies and the effectiveness of implemented actions. This will help you identify any necessary adjustments to the plan.
Identify new risks: Continuously monitor internal and external factors that could introduce new risks to the project. This includes changes in market trends, technological advancements, and regulatory updates.
Reassess priorities: As the project progresses, the priorities of identified risks may change. Regularly reassess the priority of risks and adjust your mitigation strategies accordingly.
Communicate updates: Keep all stakeholders informed of any changes to the risk management plan and involve them in the decision-making process when appropriate.
Communicate and train: Effective communication and training are key to ensuring that everyone involved in the project understands the risks and their roles in mitigating them. To empower team members to contribute effectively to risk management efforts, follow these steps:
8. Share risk information:
Clearly communicate the identified risks, their potential impact, and the mitigation strategies in place. Ensure that all team members have access to this information.
Clarify roles and responsibilities: Define the specific roles and responsibilities of each team member in relation to risk mitigation. This clarity will help them understand their part in the overall risk management process.
Provide training: Offer training sessions and resources to help team members develop the necessary skills and knowledge to manage risks effectively. This may include workshops, webinars, or access to online resources.
Encourage open communication: Foster an environment where team members feel comfortable discussing risks and sharing concerns. Encourage them to ask questions, provide feedback, and contribute to the ongoing risk management process.
9. Learn from past experiences:
Analyzing past projects and learning from successes and failures is invaluable for improving risk management processes. To use this information effectively, consider the following:
Review past projects: Examine previous projects to identify risks that were encountered, the strategies used to address them, and the outcomes of those strategies.
Identify lessons learned: Analyze past experiences to determine what worked well, what didn’t, and the reasons behind those outcomes. This analysis will help you identify best practices and areas for improvement.
Apply findings to future projects: Use the lessons learned from past projects to refine your risk management processes, making necessary adjustments to improve the effectiveness of your strategies.
Maintain a knowledge base: Create a centralized repository of risk management experiences and lessons learned, making it easily accessible to all team members. This knowledge base can serve as a valuable resource for guiding future risk management efforts.
Following these tips and maintaining a proactive approach to risk management can significantly reduce the likelihood of future risks derailing your project and achieve more predictable, successful outcomes.
How nTask assists you in developing your project’s risk management Technique?
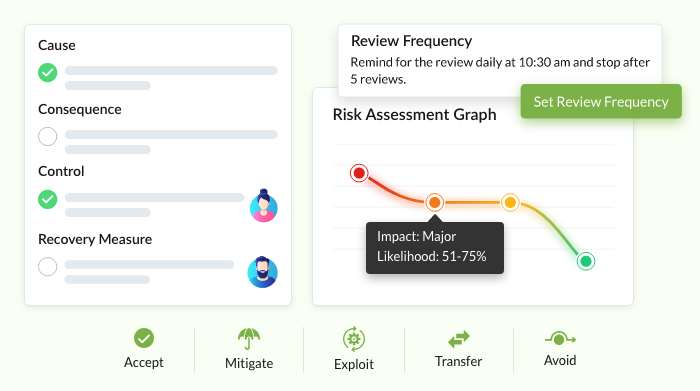
nTask has a robust risk management tool. The module allows you to identify and analyze any potential risks related to your project.
You can analyze the risk, create a risk mitigation strategy, assess the identified risk, assign it to team members, and communicate about it. nTask also creates a risk matrix for you based on your review and analysis.
With nTask’s risk management tool, you can quickly create a management plan. The management plan is maintained in a centralized location inside the project management platform alongside other key information.
Learn more about the risk management module for effective collaboration.
nTask simplifies risk management and management plan creation.
